A city paused by Vesuvius
Streets, frescoes, and domestic routines preserved under meters of volcanic debris—revealing ordinary ancient rhythms.
Table of Contents
Origins and early settlement
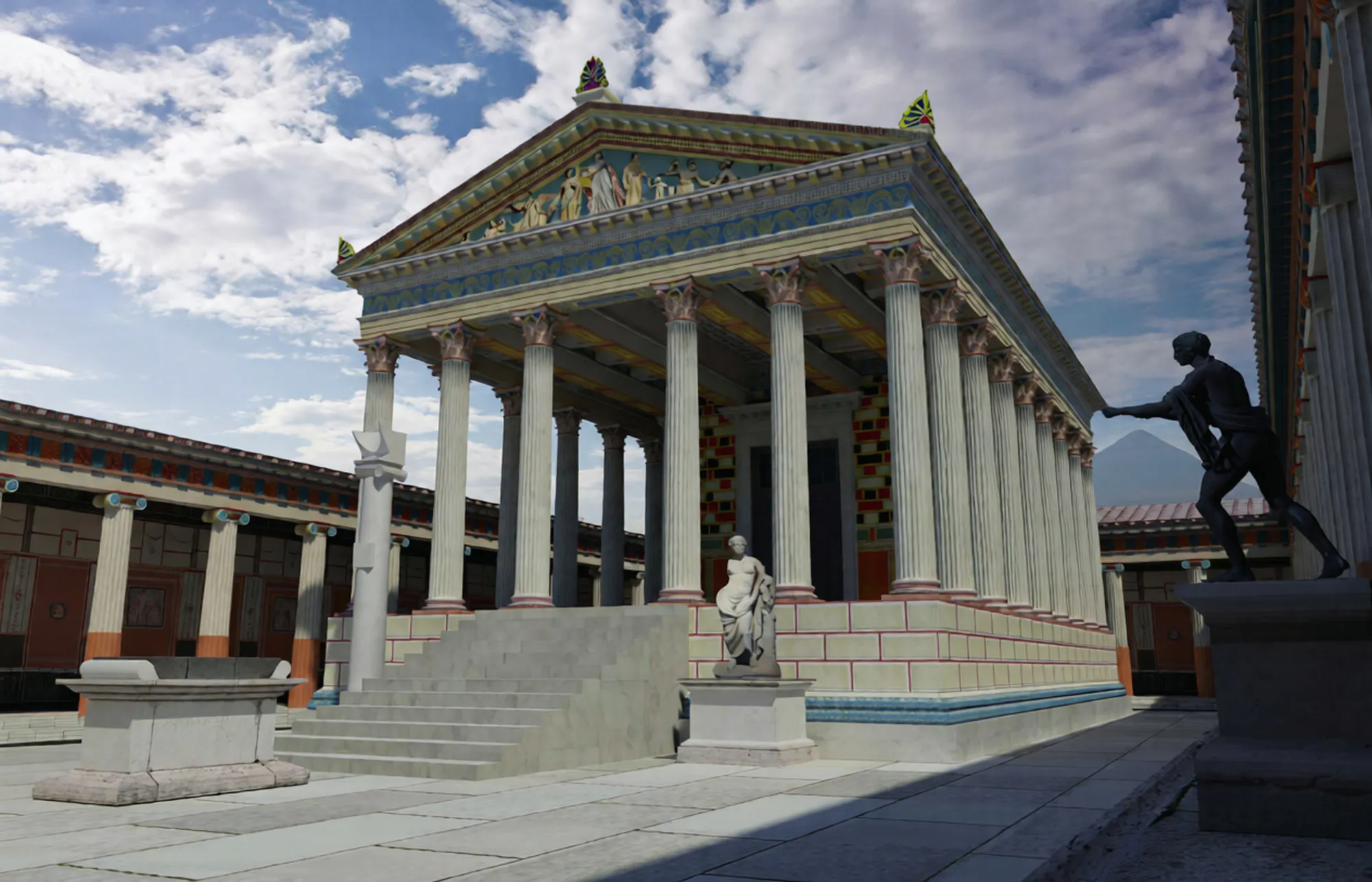

Pre‑Roman origins include Oscan and Samnite phases—strategic location near trade routes and fertile volcanic soils.
Integration into Roman sphere accelerated urban planning: forums, baths, and standardized street grids emerged.
Rome’s influence and urban growth
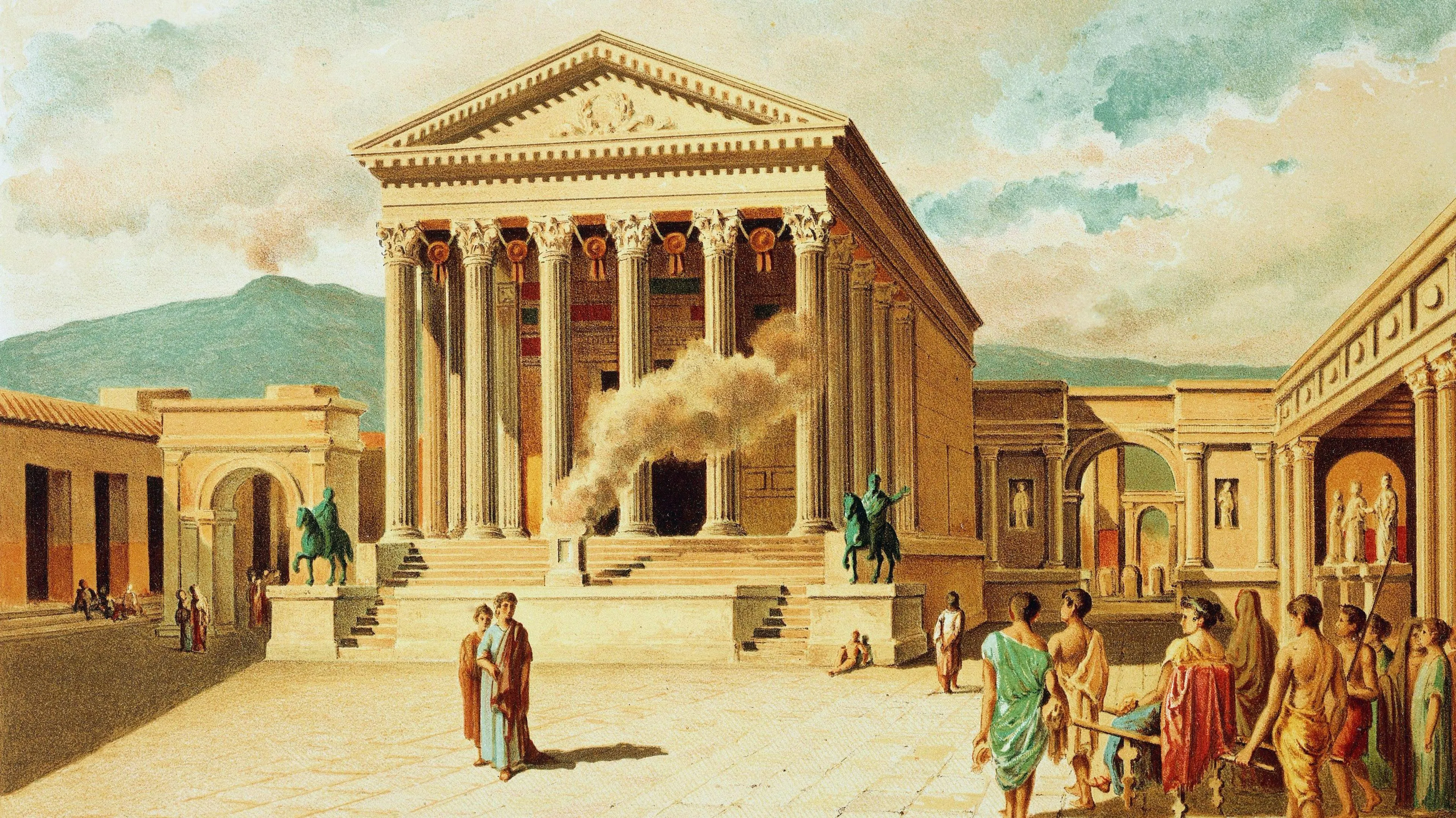
Roman administration shaped commerce, religious architecture, and civic monuments—amphitheatre and theatres entertained diverse audiences.
Economic ties stretched to Mediterranean networks—imports visible in pottery shards and luxury household artifacts.
Architecture & domestic spaces

Domus design balanced business frontage with private atrium and garden retreats—mosaics and fresco programs signaled status.
Workshops, taverns, bakeries, and fullonica laundries reveal integrated residential‑commercial mixes along busy streets.
Eruption of AD 79 timeline
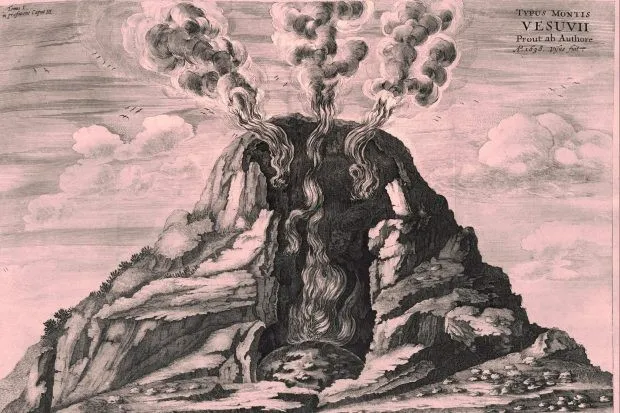

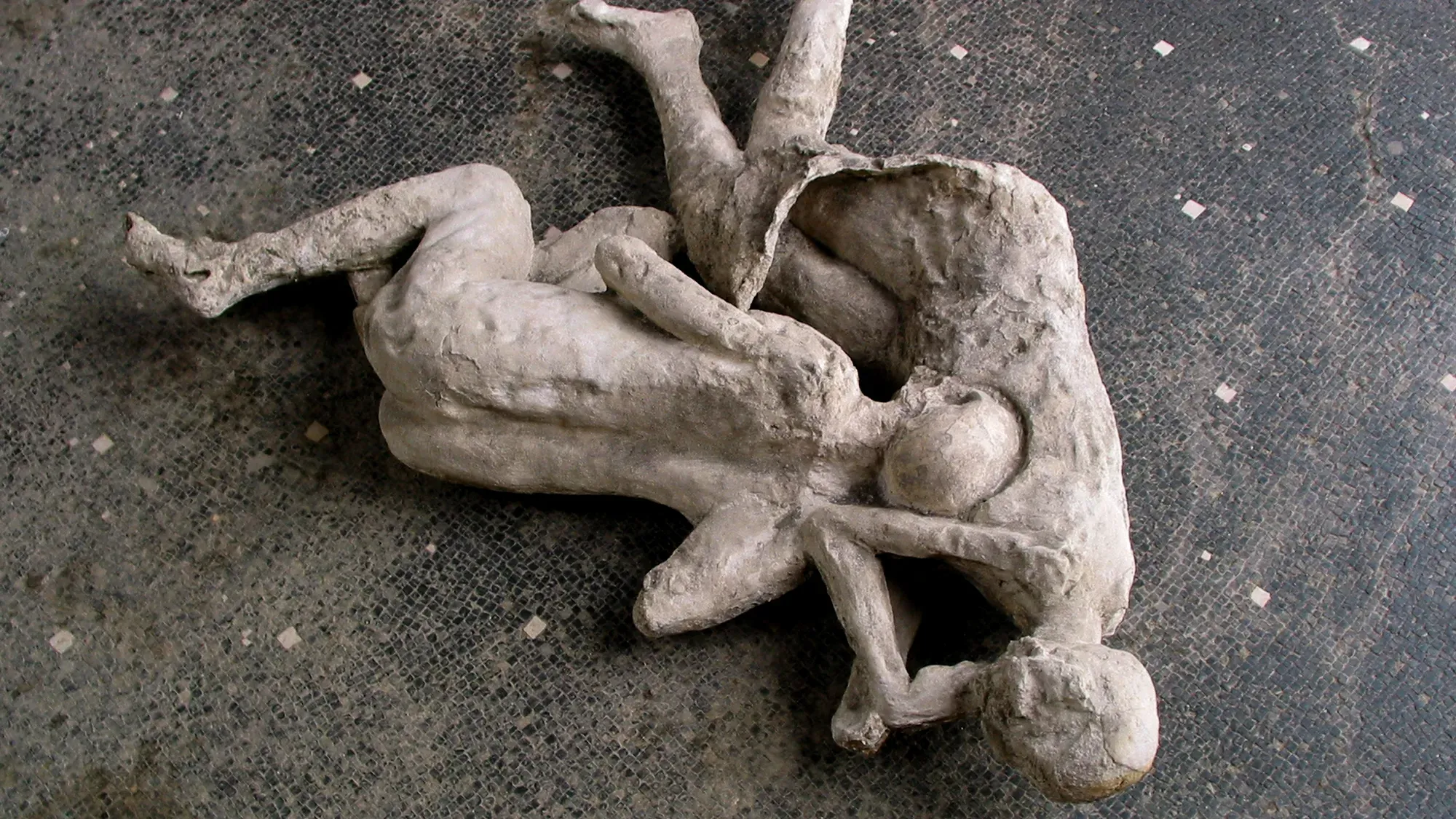
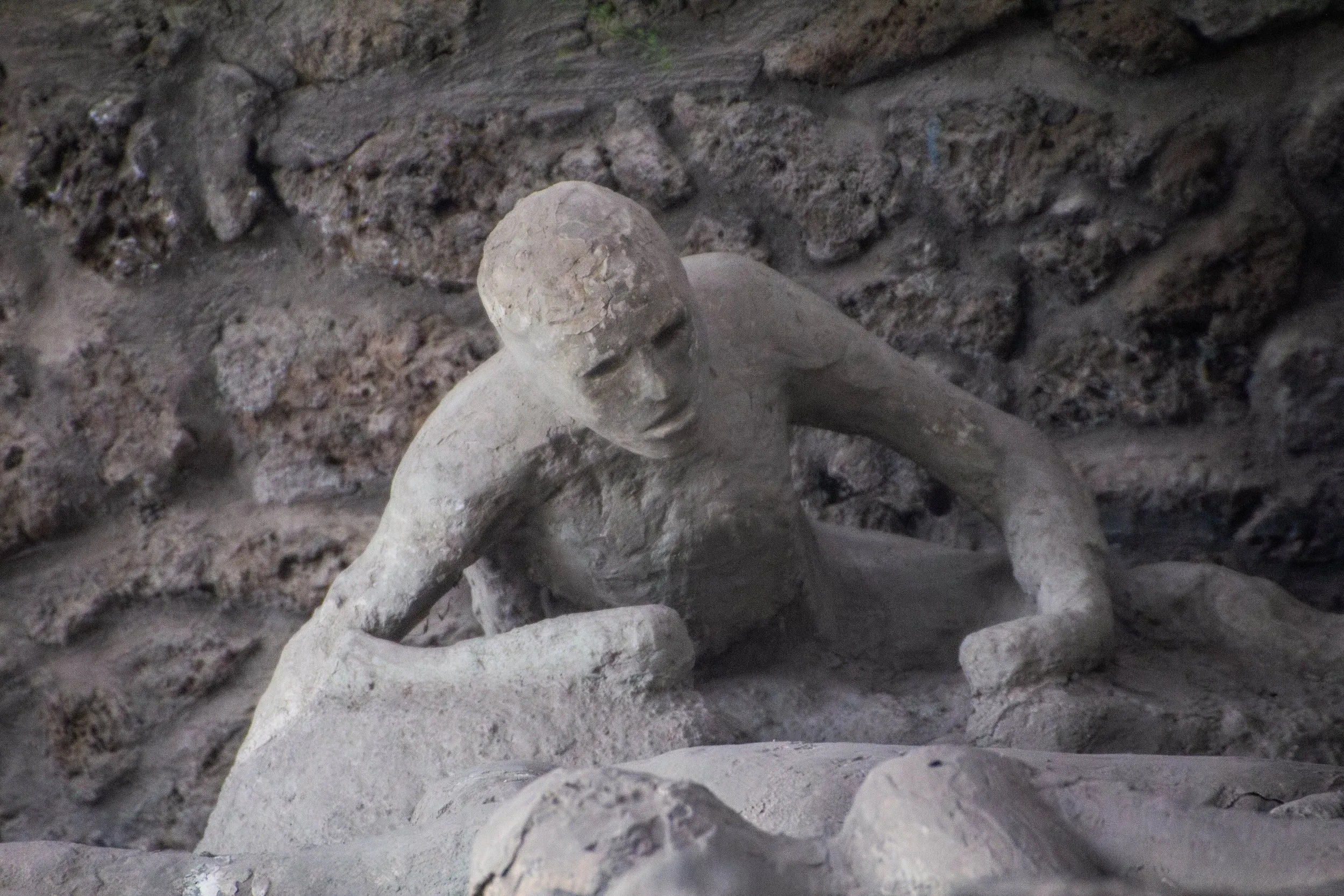
Initial pumice fall collapsed roofs; later pyroclastic surges sealed neighborhoods—tragic human story captured in voids and casts.
Preservation paradox: destructive event safeguarded urban micro‑details for future study and cultural reflection.
Daily life: work & leisure
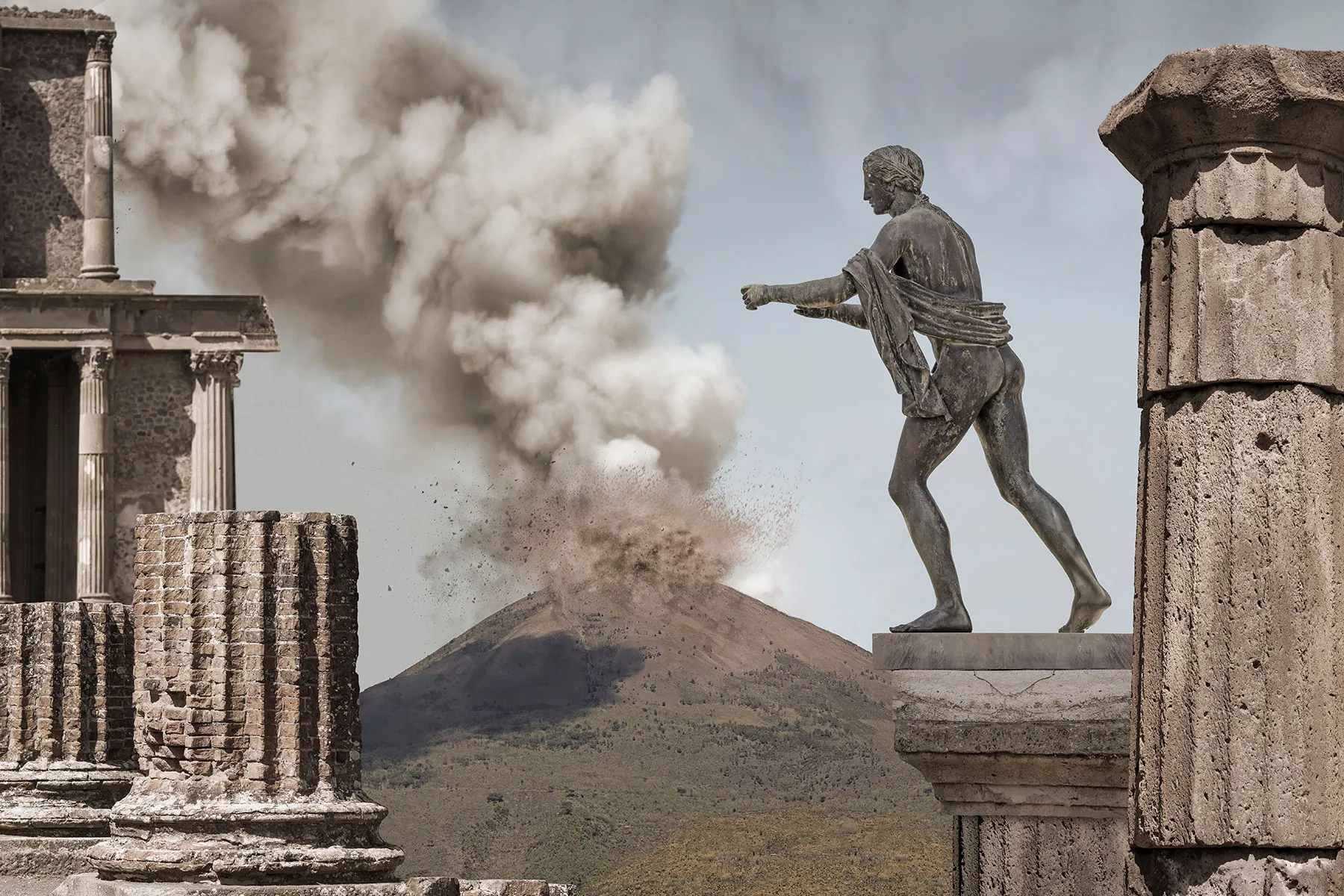

Thermopolia (street food bars), baths, and markets sustained social interaction—gladiatorial games and theatre added spectacle.
Household artifacts—lamps, amphorae, surgical tools—trace routines of health, trade, and domestic management.
Excavation & archaeological methods
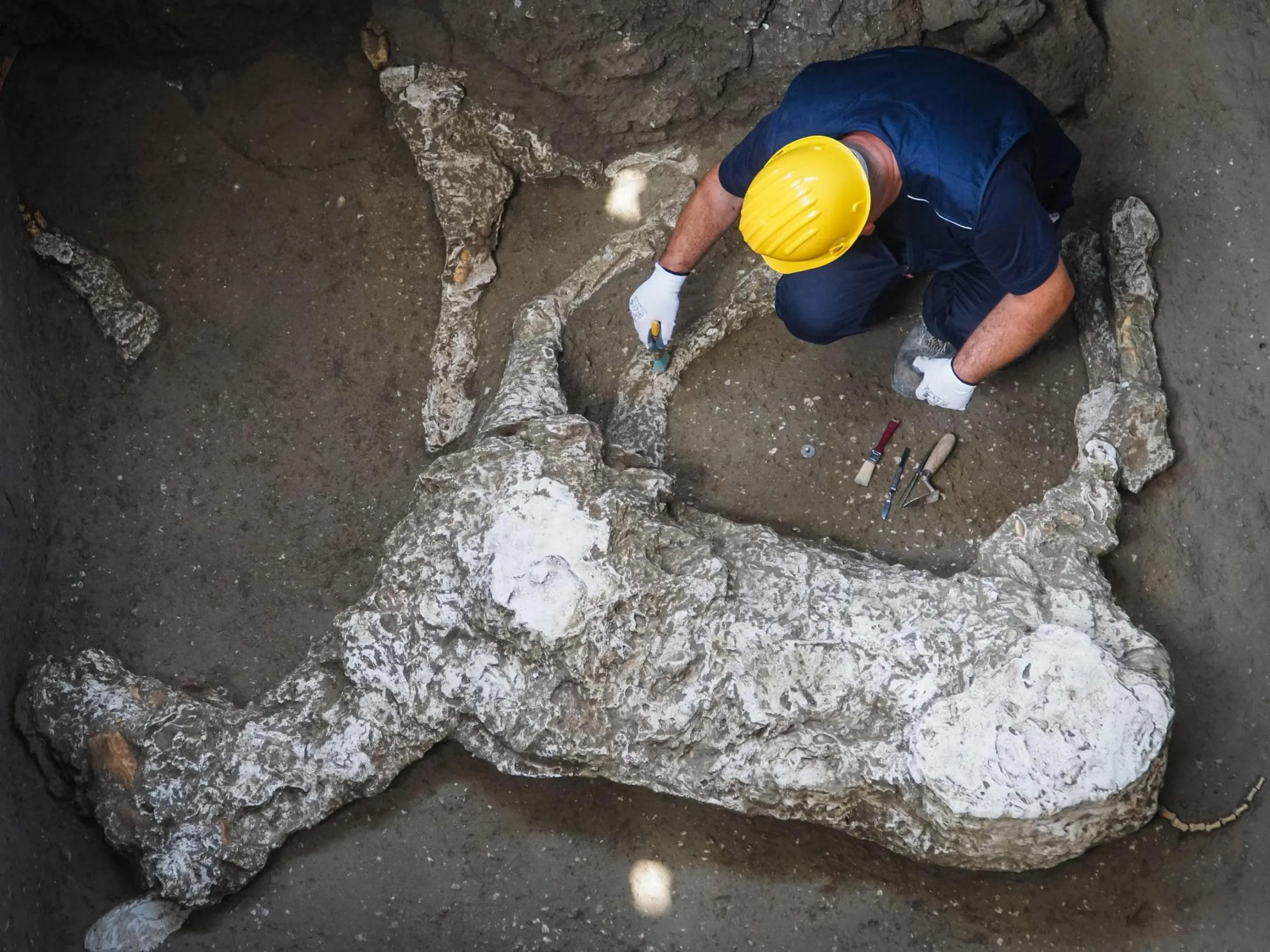

Excavations evolved from treasure focus to scientific stratigraphy—context recording now central to interpretation.
Plaster and resin cast techniques captured final forms; modern tech (3D scanning, microanalysis) refines conservation decisions.
Accessibility & visitor comfort

Improved paths and ramps in select zones aim to widen access—official maps indicate gentler routes.
Shade scarcity prompts hydration signage and rest zones—planning breaks prevents heat fatigue.
Sustainability & conservation ethics

Ongoing stabilization combats weathering and vegetation—ethical debate balances opening new areas versus protecting fragile ones.
Monitoring microclimates guides protective coverings and targeted restoration priorities.
Global fascination & imagery
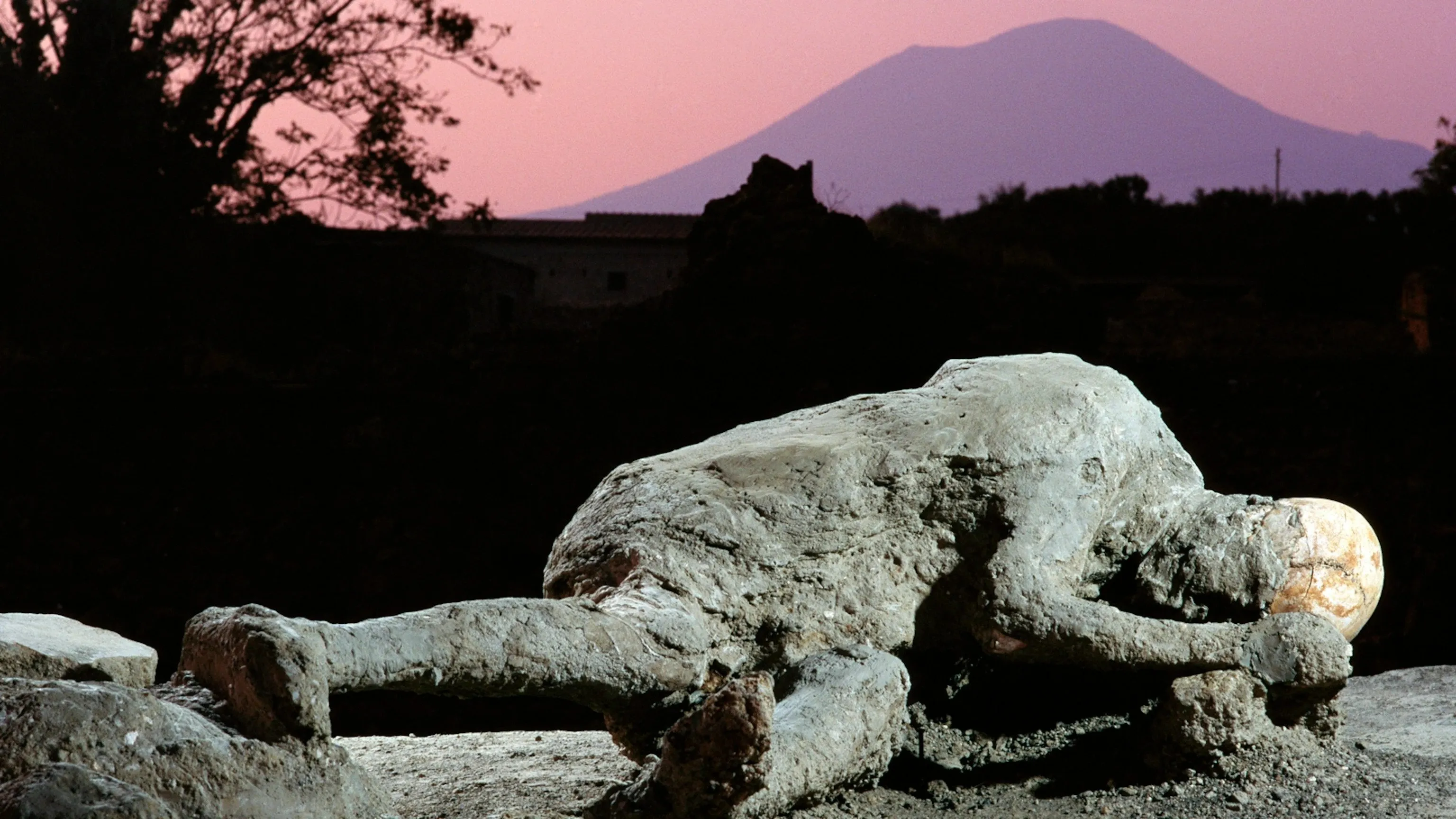

Casts and vivid wall art shaped Pompeii’s global identity—symbol of archaeology’s ability to recover everyday past.
Educational media and films reinforce emotional resonance of interrupted lives and preserved domestic scenes.
Planning with historical context
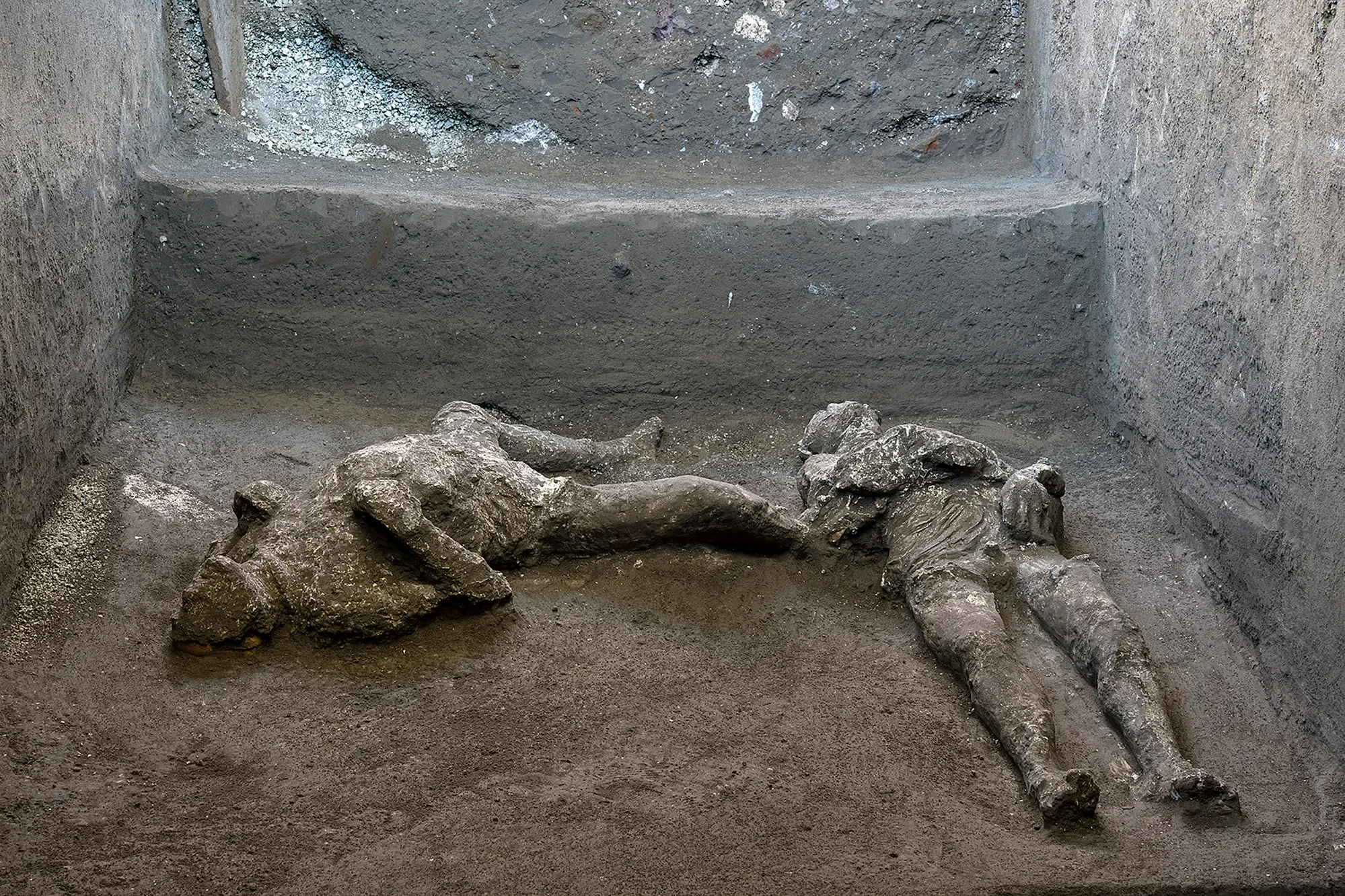

Structure your route: civic core, domestic artistry, leisure venues—context layering makes streets feel inhabited.
Observing tool marks, graffiti, and wear patterns deepens appreciation for ordinary labor rhythms.
Vesuvius and regional landscape
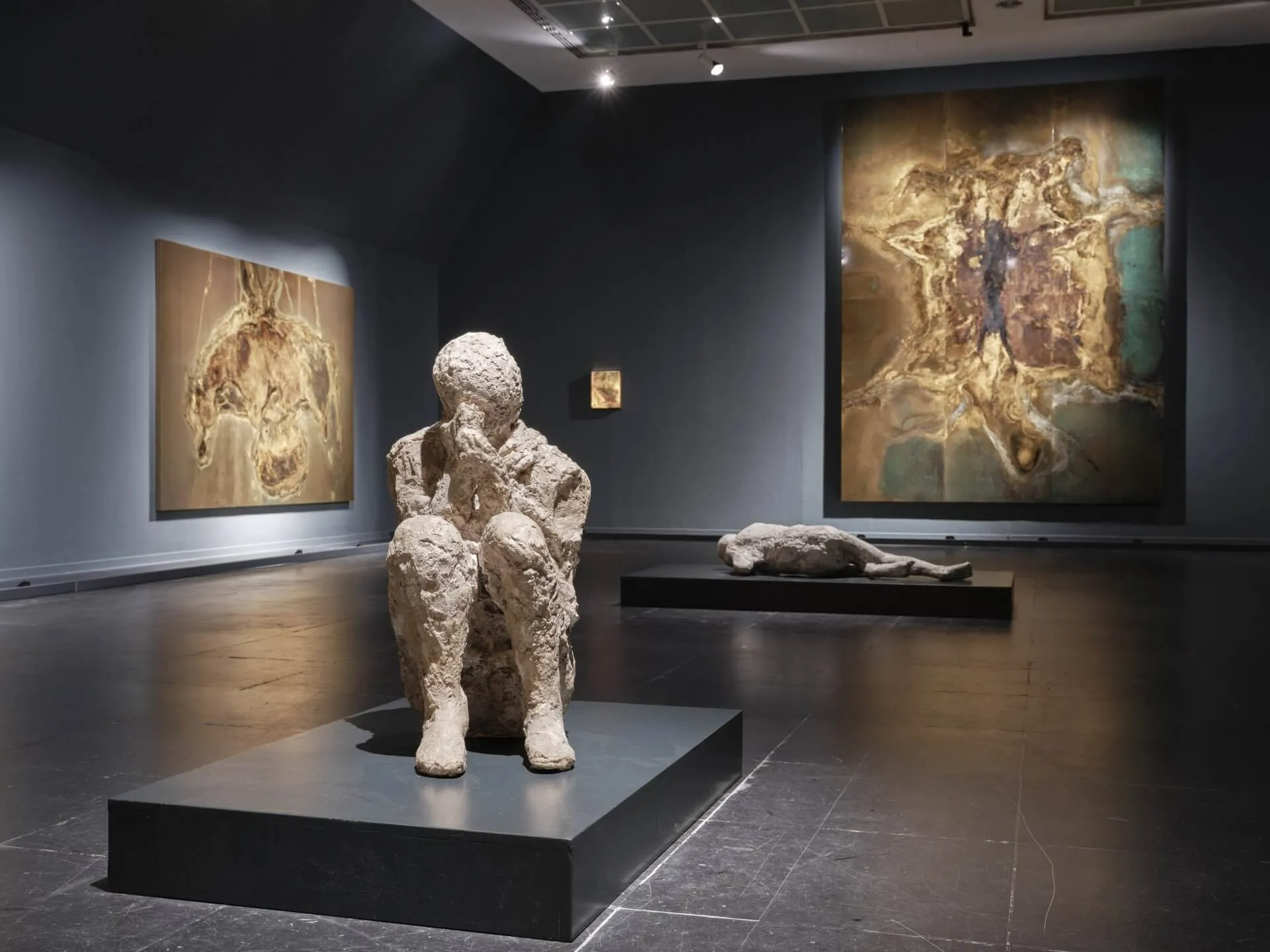

Volcanic soils supported agriculture feeding urban life—eruption cycle now studied to refine risk mapping.
Landscape walks or Vesuvius summit visits contextualize geological forces shaping settlement patterns.
Nearby complementary sites
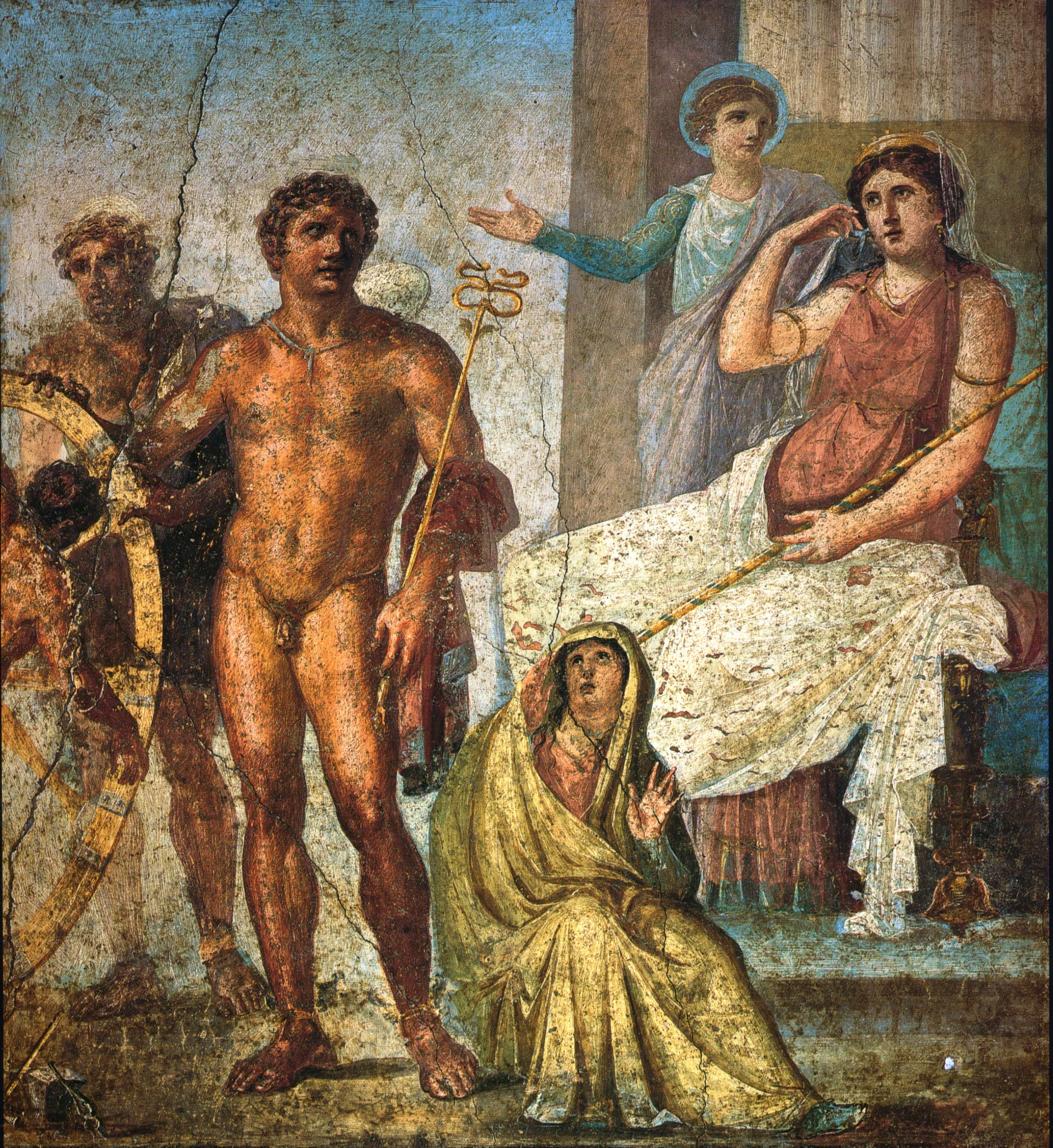

Herculaneum’s vertical preservation, Oplontis’ luxury villa, and Stabiae’s seaside retreats expand volcanic narrative.
A multi‑site itinerary reveals social strata—from elite villa art to commercial street bustle.
Enduring legacy of Pompeii
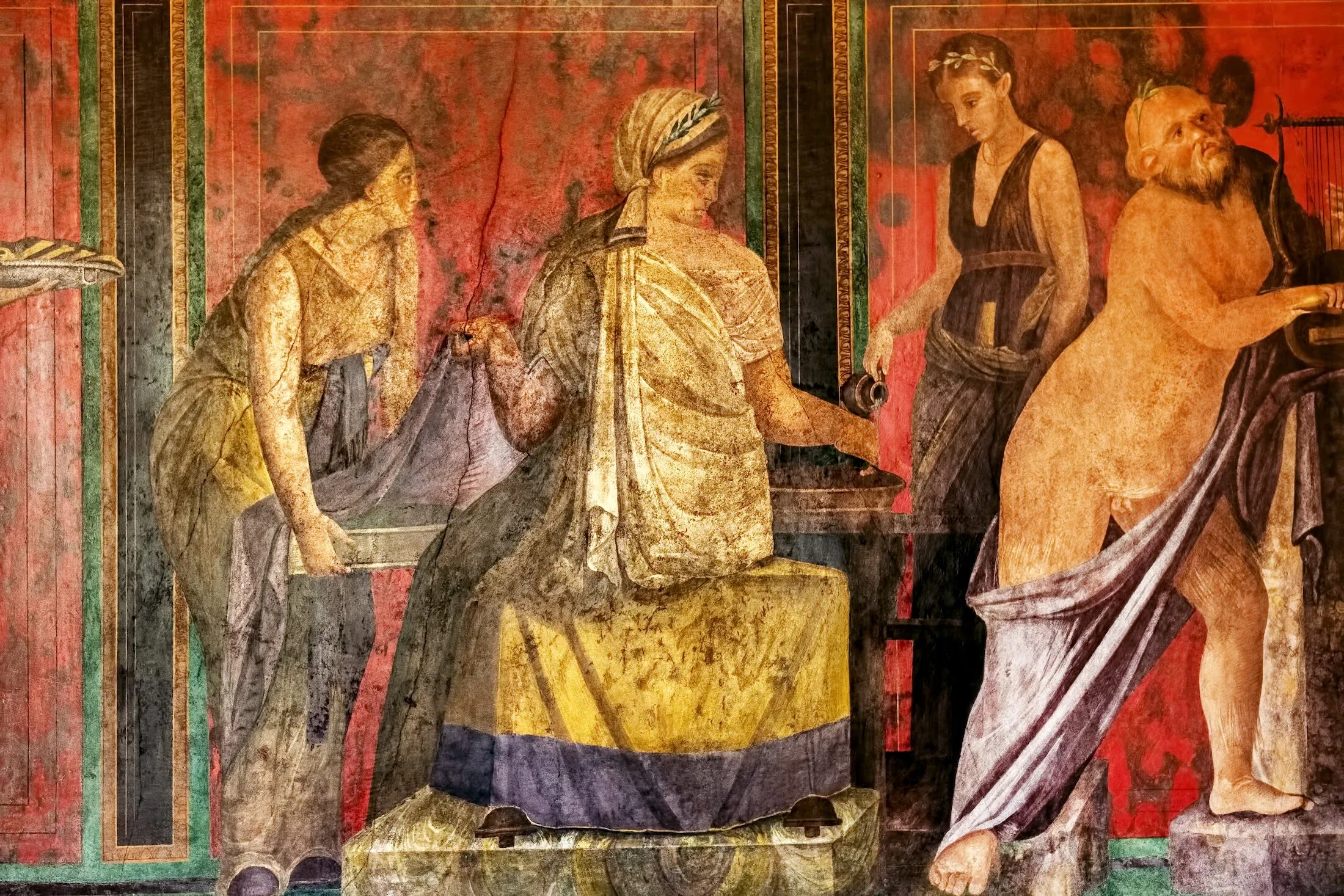

Pompeii symbolizes archaeology’s power to humanize antiquity—faces, meals, commerce moments halted yet relatable.
Continued study revises understanding of resilience, risk, and urban adaptation in ancient contexts.
Table of Contents
Origins and early settlement

Pre‑Roman origins include Oscan and Samnite phases—strategic location near trade routes and fertile volcanic soils.
Integration into Roman sphere accelerated urban planning: forums, baths, and standardized street grids emerged.
Rome’s influence and urban growth

Roman administration shaped commerce, religious architecture, and civic monuments—amphitheatre and theatres entertained diverse audiences.
Economic ties stretched to Mediterranean networks—imports visible in pottery shards and luxury household artifacts.
Architecture & domestic spaces

Domus design balanced business frontage with private atrium and garden retreats—mosaics and fresco programs signaled status.
Workshops, taverns, bakeries, and fullonica laundries reveal integrated residential‑commercial mixes along busy streets.
Eruption of AD 79 timeline

Initial pumice fall collapsed roofs; later pyroclastic surges sealed neighborhoods—tragic human story captured in voids and casts.
Preservation paradox: destructive event safeguarded urban micro‑details for future study and cultural reflection.
Daily life: work & leisure

Thermopolia (street food bars), baths, and markets sustained social interaction—gladiatorial games and theatre added spectacle.
Household artifacts—lamps, amphorae, surgical tools—trace routines of health, trade, and domestic management.
Excavation & archaeological methods

Excavations evolved from treasure focus to scientific stratigraphy—context recording now central to interpretation.
Plaster and resin cast techniques captured final forms; modern tech (3D scanning, microanalysis) refines conservation decisions.
Accessibility & visitor comfort

Improved paths and ramps in select zones aim to widen access—official maps indicate gentler routes.
Shade scarcity prompts hydration signage and rest zones—planning breaks prevents heat fatigue.
Sustainability & conservation ethics

Ongoing stabilization combats weathering and vegetation—ethical debate balances opening new areas versus protecting fragile ones.
Monitoring microclimates guides protective coverings and targeted restoration priorities.
Global fascination & imagery

Casts and vivid wall art shaped Pompeii’s global identity—symbol of archaeology’s ability to recover everyday past.
Educational media and films reinforce emotional resonance of interrupted lives and preserved domestic scenes.
Planning with historical context

Structure your route: civic core, domestic artistry, leisure venues—context layering makes streets feel inhabited.
Observing tool marks, graffiti, and wear patterns deepens appreciation for ordinary labor rhythms.
Vesuvius and regional landscape

Volcanic soils supported agriculture feeding urban life—eruption cycle now studied to refine risk mapping.
Landscape walks or Vesuvius summit visits contextualize geological forces shaping settlement patterns.
Nearby complementary sites

Herculaneum’s vertical preservation, Oplontis’ luxury villa, and Stabiae’s seaside retreats expand volcanic narrative.
A multi‑site itinerary reveals social strata—from elite villa art to commercial street bustle.
Enduring legacy of Pompeii

Pompeii symbolizes archaeology’s power to humanize antiquity—faces, meals, commerce moments halted yet relatable.
Continued study revises understanding of resilience, risk, and urban adaptation in ancient contexts.